The Future of Cloud Computing: Trends and Innovations in 2024
Cloud computing has revolutionized the way businesses operate, offering unprecedented scalability, flexibility, and cost-efficiency. Therefore, as technology advances more and more, the cloud is experiencing various transformations. Now let’s take a closer look at what the main trends and novelties are that the cloud computing market will follow in 2024.
Introduction
Cloud computing is an innovative technology that provides access to shared computer resources and software through a network rather than through hardware devices. It includes everything from computing storage space and CPU cycles, to software applications, and these are all delivered according to user need and usually based on use with pay-per-use fees. This model enables organizations as well as people to use and grow resources provided at their disposal with much ease, without having to invest heavily in capital equipment and programs. Cloud computing is important today, as it contributes to the speed of application delivery, fosters teamwork, and encourages innovation in different fields. Cloud services can help minimize costs, increase organizational productivity, and allow organizations to concentrate on their key activities, thus being an essential part of contemporary IT solutions.
Current Trends in Cloud Computing
-
AI and Machine Learning Integration
AI and ML are remarkably positively impacting the value proposition that cloud services offer by now automating large processes, analyzing data more efficiently, and creating prediction models. These technologies are resource management efficient, can detect security anomalies, and facilitate more personalized user experiences. For instance, popular cloud applications such as AWS SageMaker or Google Cloud AI offer instruments to create, train, and release ML models in the cloud.
-
Edge Computing
Edge computing, therefore, refers to a paradigm where data processing takes place near a data source and not in a centralized data processing centre. This approach minimizes latencies, increases real-time data handling, and optimizes bandwidth utilization. The use cases are self-driving cars, where detection and interaction with the environment need to happen in real-time, and smart cities, where traffic control, surveillance, and security systems depend on edge computing efficiency.
-
Hybrid and Multi-Cloud Strategies
Hybrid and Multi-cloud solutions connect private and public clouds, whereby an organization can enjoy both realms. Hybrid cloud refers to the use of the organization’s infrastructure together with services that are based in the cloud to deliver more capabilities and more management in the architecture. Multi-Cloud is the act of using cloud services from different providers as a way of avoiding being /locked/to certain service providers and maximizing on capabilities. These strategies, as well as having advantages like better disaster recovery and cost control, also come with disadvantages, including the complexity of management and possible security issues.
Security and Compliance in the Cloud

Latest Security Measures
- Data Encryption and Access Control: In current advanced cloud security, data encryption algorithm is used extensively to ensure security to an enormous extent, not only in data transmission but also when it is idle in the cloud. Sub-processes of mandatory access control, identification, and authentication, such as multi-factor authentication and role-based access control, guarantee restricted accessibility.
- Innovations in Cloud Security: Recent innovations include the application of artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms in threat identification and prevention, assuming no trust in any particular device or segment within the network, and SASE solutions for improving security in the dynamic edge environment.
Compliance and Regulatory Challenges
- Key Regulations Affecting Cloud Computing: Companies face and have to meet different Regulations like GDPR in Europe, the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) in the U. S. and PCI DSS. These regulations also require the data safeguarding and privacy measures concerning the individual to be strict.
- Strategies for Maintaining Compliance: Therefore, businesses should actively implement elaborate governance structures, followed by the possibility of auditing and updating about regulatory changes. Outsourcing regulatory compliance to CSPs who have certified compliance solutions can also enhance the management of regulatory needs.
Cost Management and Optimization
Cloud Cost Optimization Techniques
- Best Practices for Reducing Cloud Expenses: Some of the measures that companies need to take to reduce costs incurred on the cloud include: right scalling for resources where actual usage is low, reserved instances particularly for those businesses which have established workloads that do not vary very much over time, and auto-scaling; this is because resources can be scaled up or down depending on the demands placed. Further, it is possible to reduce costs substantially by a routine check and elimination of recklessly adopted or infrequently employed resources that are no longer in requisite.
- Tools and Services for Cost Management: There are some Cost Management Tools and Services that can be used to better manage Cloud Costs. For instance, AWS offers AWS Cost Explorer, while Azure has Azure Cost Management, and Google Cloud has Google Cloud’s Cost Management tools that help to parse the expenses and suggest ways of cost reduction. Third-party tools such as Cloud Health and Cloudability also integrate cost management into their set of capabilities.
FinOps: Financial Operations in the Cloud
- Introduction to FinOps: FinOps is a practice that aligns finance with cloud operations, which helps you maximize the value of cloud investments. It entails the effort of the finance department, the engineering department, and the operations team in the process of managing costs incurred in the cloud.
- Benefits of Adopting FinOps Practices: Looking at how to improve cloud spending and control, FinOps methodologies can be used to gain better visibility and control of cloud costs, planning, and forecasting of expenditure, and to drive organizational accountability across teams. Intrinsic, organizations can derive optimum value out of the cloud by cultivating organizational consciousness that diagnoses and deals with cost.
Industry-Specific Cloud Solutions
Here’s a detailed introduction to industry-specific cloud solutions for healthcare, finance, and retail:
Healthcare
Cloud Applications in Healthcare:
Cloud computing in healthcare involves using cloud platforms to store, manage, and process medical data. This includes electronic health records (EHRs), telehealth services, and AI-driven diagnostics. Cloud solutions enable healthcare providers to access patient data securely from anywhere, facilitating better coordination and continuity of care.
Benefits for Patient Care and Data Management:
- Enhanced Data Accessibility: Cloud platforms allow healthcare professionals to access patient records and medical histories in real-time, improving decision-making and patient outcomes.
- Cost Efficiency: By reducing the need for physical servers and IT infrastructure, cloud computing lowers operational costs.
- Improved Collaboration: Cloud-based systems enable seamless sharing of information among healthcare providers, enhancing collaborative care.
- Data Security: Advanced encryption and compliance with healthcare regulations ensure that patient data is protected.
Finance
Cloud Computing in the Financial Sector:
Financial institutions use cloud computing to manage vast amounts of data, streamline operations, and enhance customer services. Cloud platforms support everything from transaction processing to risk management and regulatory compliance.
Enhancing Security and Efficiency:
- Robust Security Measures: Cloud providers offer advanced security features, including encryption, multi-factor authentication, and compliance with financial regulations.
- Operational Efficiency: Cloud computing reduces the need for physical infrastructure, leading to significant cost savings and operational flexibility.
- Scalability: Financial institutions can easily scale their IT resources up or down based on demand, ensuring they can handle peak loads without over-investing in infrastructure.
- Disaster Recovery: Cloud solutions provide reliable backup and disaster recovery options, ensuring business continuity in case of data loss or cyberattacks.
Retail
Cloud Solutions for Retail Businesses:
Retailers leverage cloud computing to enhance customer experiences, optimize operations, and drive sales. Cloud platforms support e-commerce, inventory management, and personalized marketing.
Improving Customer Experience and Operations:
- Personalized Shopping Experiences: By analyzing customer data, retailers can offer personalized recommendations and promotions, improving customer satisfaction.
- Efficient Inventory Management: Cloud-based systems provide real-time inventory tracking, reducing stockouts and overstock situations.
- Omnichannel Integration: Cloud solutions enable seamless integration of online and offline channels, providing a consistent shopping experience across all touchpoints.
- Cost Reduction: By moving to the cloud, retailers can reduce IT infrastructure costs and focus more on strategic initiatives.
These industry-specific cloud solutions are transforming how businesses operate, making them more efficient, secure, and customer-centric.
Types of Cloud Computing
Cloud computing can be categorized into several types based on deployment models and services offered.
Here’s a detailed introduction to the types of cloud computing, private cloud computing, and virtualization in cloud computing, along with additional information on other types of cloud computing:
- Public Cloud:
-
-
- Description: Public clouds are operated by third-party cloud service providers and deliver computing resources over the internet. Examples include Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform.
- Benefits: Cost-effective, scalable, and easy to deploy. Suitable for businesses that do not require high levels of security and control.
-
- Private Cloud:
-
-
- Description: A private cloud is dedicated to a single organization, providing greater control and security. It can be hosted on-premises or by a third-party provider.
- Benefits: Enhanced security, customization, and control over data and resources.
-
- Hybrid Cloud:
-
-
- Description: Combines public and private clouds, allowing data and applications to be shared between them. This provides greater flexibility and optimization of existing infrastructure.
- Benefits: Balances the need for security and scalability, enabling businesses to handle varying workloads efficiently.
-
- Multi Cloud:
-
-
- Description: Involves using multiple cloud services from different providers. This approach helps avoid vendor lock-in and allows businesses to leverage the best features of each provider.
- Benefits: Increased flexibility, risk mitigation, and the ability to optimize costs and performance.
-
- Community Cloud:
-
- Description: A cloud infrastructure shared by several organizations with common concerns, such as security, compliance, or jurisdiction.
- Benefits: Cost-sharing, collaborative efforts, and tailored solutions for specific community needs.
Private Cloud Compute
Private Cloud:
A private cloud is a cloud computing environment dedicated to a single organization. It offers the same benefits as public clouds, such as scalability and self-service, but with added control and security. Private clouds can be hosted on-premises or by a third-party provider.
Benefits:
- Enhanced Security: Since resources are not shared with other organizations, private clouds offer higher levels of security and compliance.
- Customization: Organizations can tailor the cloud environment to meet their specific needs and requirements.
- Control: Greater control over data, applications, and resources, allowing for better management and optimization.
Virtualization in Cloud Computing
Virtualization:
Virtualization is a technology that allows multiple virtual machines (VMs) to run on a single physical server. Each VM operates independently, with its own operating system and applications. This technology is fundamental to cloud computing as it enables efficient resource utilization and scalability.
Benefits:
- Resource Optimization: Virtualization allows for better utilization of physical hardware, reducing the need for additional servers.
- Scalability: Easily scale resources up or down based on demand without the need for physical hardware changes.
- Isolation: Each VM is isolated from others, ensuring that issues in one VM do not affect others.
- Cost Savings: Reduces the need for physical infrastructure, leading to lower operational costs.
Additional Types of Cloud Computing Services
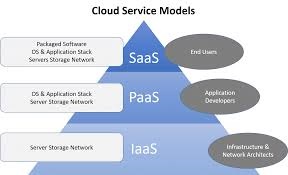
- Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS):
-
-
- Description: Provides virtualized computing resources over the Internet. Users can rent virtual machines, storage, and networks.
- Examples: AWS EC2, Google Compute Engine.
-
- Platform as a Service (PaaS):
-
-
- Description: Offers hardware and software tools over the internet. PaaS is used for application development without managing the underlying infrastructure.
- Examples: Google App Engine, Microsoft Azure App Services.
-
- Software as a Service (SaaS):
-
-
- Description: Delivers software applications over the internet on a subscription basis. Users can access applications via web browsers.
- Examples: Salesforce, Microsoft Office.
-
- Serverless Computing:
-
- Description: Allows developers to build and run applications without managing the underlying infrastructure. The cloud provider automatically handles the server management.
- Examples: AWS Lambda, Google Cloud Functions.
These various types of cloud computing and services offer different benefits and can be chosen based on specific business needs and goals.
Future Predictions and Innovations
Here’s a detailed introduction to future predictions and innovations in cloud computing, focusing on quantum computing and sustainability:
Quantum Computing and the Cloud
- Potential Impact of Quantum Computing on Cloud Services: The application of quantum computing can redesign and transform cloud services by solving problems that are too big for classical computers to solve. This comprises the fine-tuning of macaque-scale systems, the improvement of cryptographic security, and the speed up of machine learning algorithms. Quantum cloud computing provides enterprises with access to quantum computing facilities with no need for specific equipment and ensures the availability of advanced computational capabilities.
- Current Research and Developments: Prominent quantum cloud computing advances were the establishment of quantum algorithms, quantum error correction, and the quantum-classical approach. The giants like IBM, Google, and Microsoft have come up with their quantum cloud platforms, for example, IBM Quantum Experience and Microsoft Azure Quantum. Quantum coherence is one area of concern for researchers. The error rate and producing real-world applications across various sectors such as the drugstore, finance sector, and logistics, among others.
Sustainability in Cloud Computing
- Green Cloud Initiatives: Green cloud strategy is thus becoming the common norm for different cloud providers as they seek to minimize their ecological footprint. Such measures include the utilization of renewable energy resources, the efficient utilization of the data centre, and other carbon-neutral programmes being undertaken. To illustrate it, Google Cloud, with its parent company Alphabet, has pledged to run the services on carbon-free energy by the year 2030, while Microsoft has set a goal for the company to become carbon negative without any strife by 2030.
How Cloud Providers Are Reducing Their Carbon Footprint:
- Renewable Energy: Many cloud providers are investing in renewable energy projects, such as solar and wind farms, to power their data centres.
- Energy Efficiency: Data centres are being designed with advanced cooling systems, energy-efficient hardware, and AI-driven energy management to reduce power consumption.
- Carbon Offsetting: Providers are purchasing carbon credits and investing in reforestation and other carbon offset projects to neutralize their carbon emissions.
- Sustainable Practices: Initiatives like recycling electronic waste, reducing water usage, and promoting circular economy practices are being implemented to further minimize environmental impact.
These innovations and initiatives are shaping the future of cloud computing, making it more powerful and sustainable.
Facts About Cloud Computing Service, Certification, Salary
Here’s a detailed introduction to cloud computing services, certifications, and salaries:
Cloud Computing Service
Cloud Computing Service: Cloud computing services provide on-demand access to computing resources such as servers, storage, databases, networking, software, and analytics over the internet. These services are typically categorized into three main types:
-
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS):
-
-
- Description: Provides virtualized computing resources over the internet. Users can rent virtual machines, storage, and networks.
- Examples: Amazon Web Services (AWS) EC2, Google Compute Engine.
-
-
Platform as a Service (PaaS):
-
-
- Description: Offers hardware and software tools over the internet. PaaS is used for application development without managing the underlying infrastructure.
- Examples: Google App Engine, Microsoft Azure App Services.
-
-
Software as a Service (SaaS):
-
- Description: Delivers software applications over the internet on a subscription basis. Users can access applications via web browsers.
- Examples: Salesforce, Microsoft Office 365.
Cloud Computing Certification
Cloud Computing Certification: Cloud computing certifications validate an individual’s expertise in cloud technologies and platforms. These certifications are offered by major cloud service providers and are highly valued in the IT industry. Some of the top certifications include:
-
Google Certified Professional Cloud Architect:
-
-
- Description: Validates the ability to design, develop, and manage robust, secure, scalable, and dynamic solutions on Google Cloud Platform.
- Average Salary: $139,000–$175,000 USD.
-
-
Microsoft Certified Azure Solutions Architect Expert:
-
-
- Description: Demonstrates expertise in designing and implementing solutions that run on Microsoft Azure, including aspects like compute, network, storage, and security.
- Average Salary: $135,000–$150,000 USD.
-
-
AWS Certified Solutions Architect – Associate:
-
- Description: Validates the ability to design and deploy scalable systems on AWS.
- Average Salary: $130,000–$140,000 USD.
Cloud Computing Salary
Cloud Computing Salary: Salaries in cloud computing vary based on the role, experience, and location. However, cloud computing professionals generally command high salaries due to the demand for their skills. Here are some average salaries for common cloud computing roles:
-
Cloud Engineer:
-
-
- Description: Responsible for designing, implementing, and managing cloud-based systems.
- Average Salary: $116,780 USD per year.
-
-
Cloud Architect:
-
-
- Description: Designs and oversees the cloud computing strategy, including cloud adoption plans, cloud application design, and cloud management and monitoring.
- Average Salary: $135,000–$175,000 USD per year.
-
-
Cloud Developer:
-
- Description: Develops applications and services for cloud platforms.
- Average Salary: $99,881 USD per year.
These certifications and roles highlight the growing importance and lucrative nature of careers in cloud computing.
Conclusion
Cloud computing undoubtedly changes the technological world by giving power to enterprises or individuals. They have scaled and are innovative on-demand availability of needed resources due to their flexibility for so many industries. The application of AI and machine learning, the emergence of the edge computing concept, as well as the use of a hybrid and multi-cloud model, are changing the cloud computing environment.
Security and compliance issues remain a critical consideration as organizations grapple with issues related to do with data protection. Overall cost optimization especially requires a more notable systematic approach in cost management, which entails the adoption of FinOps. Platform-specific cloud services prove that it is possible to significantly change the healthcare, finance, and retail industries.
Ahead, two of the most progressing technologies, Quantum computing and cloud computing, shall open vast possibilities for sheer problem-solving and innovations. Further, the shift towards sustainability is not only helping organizations but forcing cloud providers to rein in their emissions and go green.
For organizations to maximize cloud computing potential, they have to recruit talent keen on the concept as well as the right certification. Thus, the companies must be aware of the trends and novelty to make the right decision in the right direction and earn a competitive advantage. The prospects of cloud computing’s future can be seen as rather rosy, as there appears to be no limit to the cloud’s potential for evolution and reinvention. When decision-makers see cloud computing as a deceptively simple enabler, they are opening up new possibilities for new opportunities, productivity advancement, and innovation.


